

















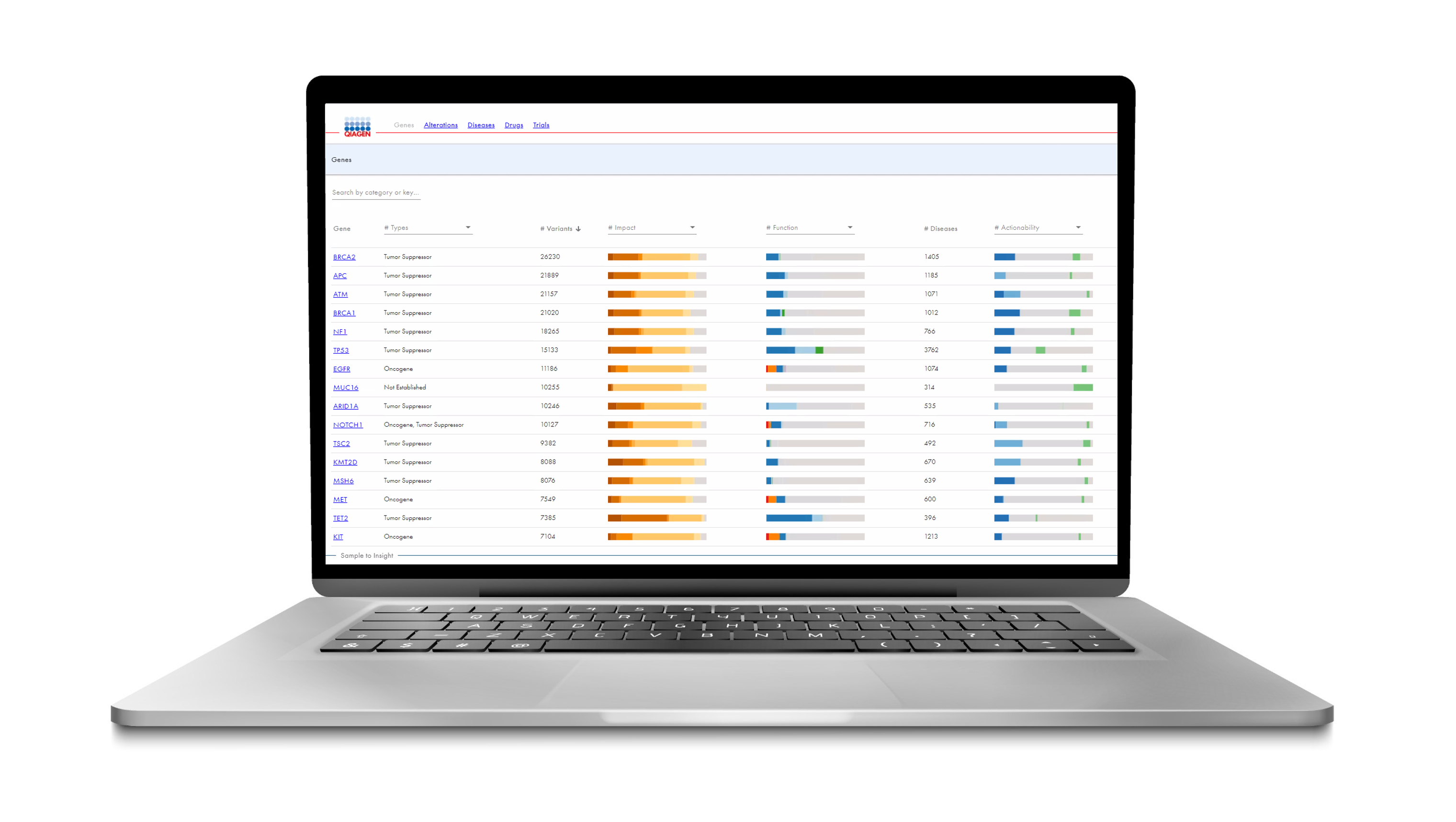
The Human Somatic Mutation Database (HSMD) is a new somatic database developed by QIAGEN that contains extensive genomic content relevant to solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
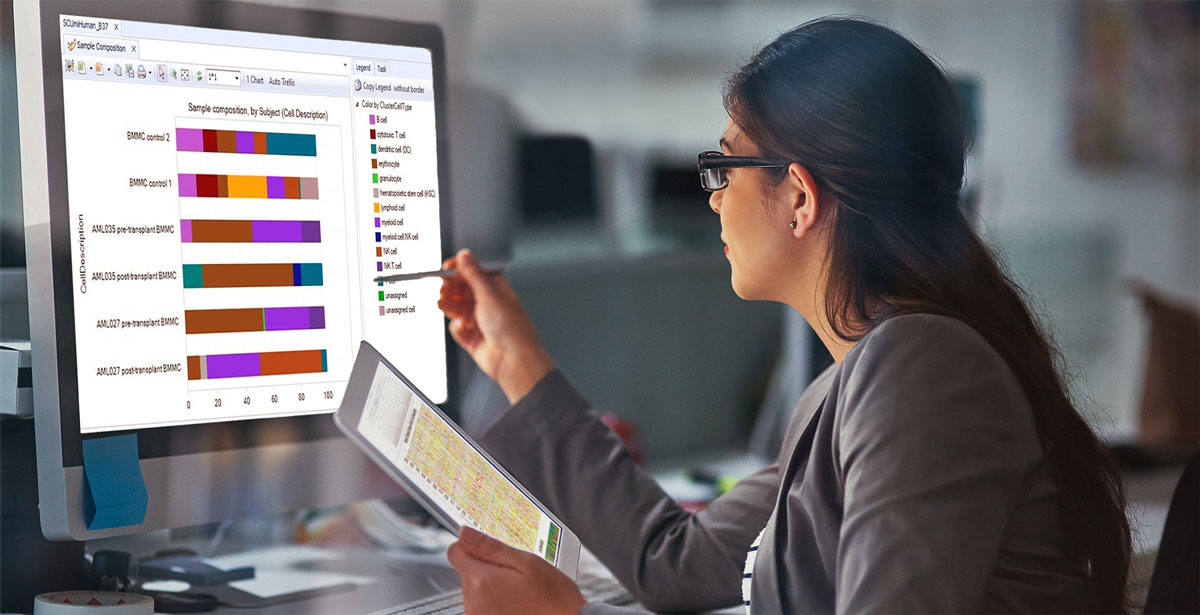
In the latest version of HSMD, the resource focuses on providing deep insight into small variants, such as SNVs, indels, frameshifts, fusions and copy number variants that have been clinically observed or curated from scientific literature to help users better understand and define precise function and actionability.
Available as a web-based application, this expert-curated resource contains content from over 500,000 real-world clinical oncology cases combined with content from the QIAGEN Knowledge Base (QKB), providing gene-level, alteration-level, and disease-level information.
HSMD leverages variant content from two sources: expert-curated content from the QIAGEN Knowledge Base (QKB) and data from real-world oncology cases sourced from our professional clinical interpretation services.
Users can easily search and explore mutational characteristics across genes, synthesize key findings from drug labels, clinical trials, and professional guidelines, and receive detailed annotations for each observed variant.
When a variant has been “clinically observed,” it means our professional clinical interpretation service has encountered this alteration in a real-world clinical case.
For these variants, our team has assessed the clinical and biological relevance and calculated the gene and variant prevalence across observed tumor types.
Conversely, content from the QKB is proactively curated from scientific literature; therefore, not all variants have yet been directly clinically observed by our professional clinical interpretation services.