

















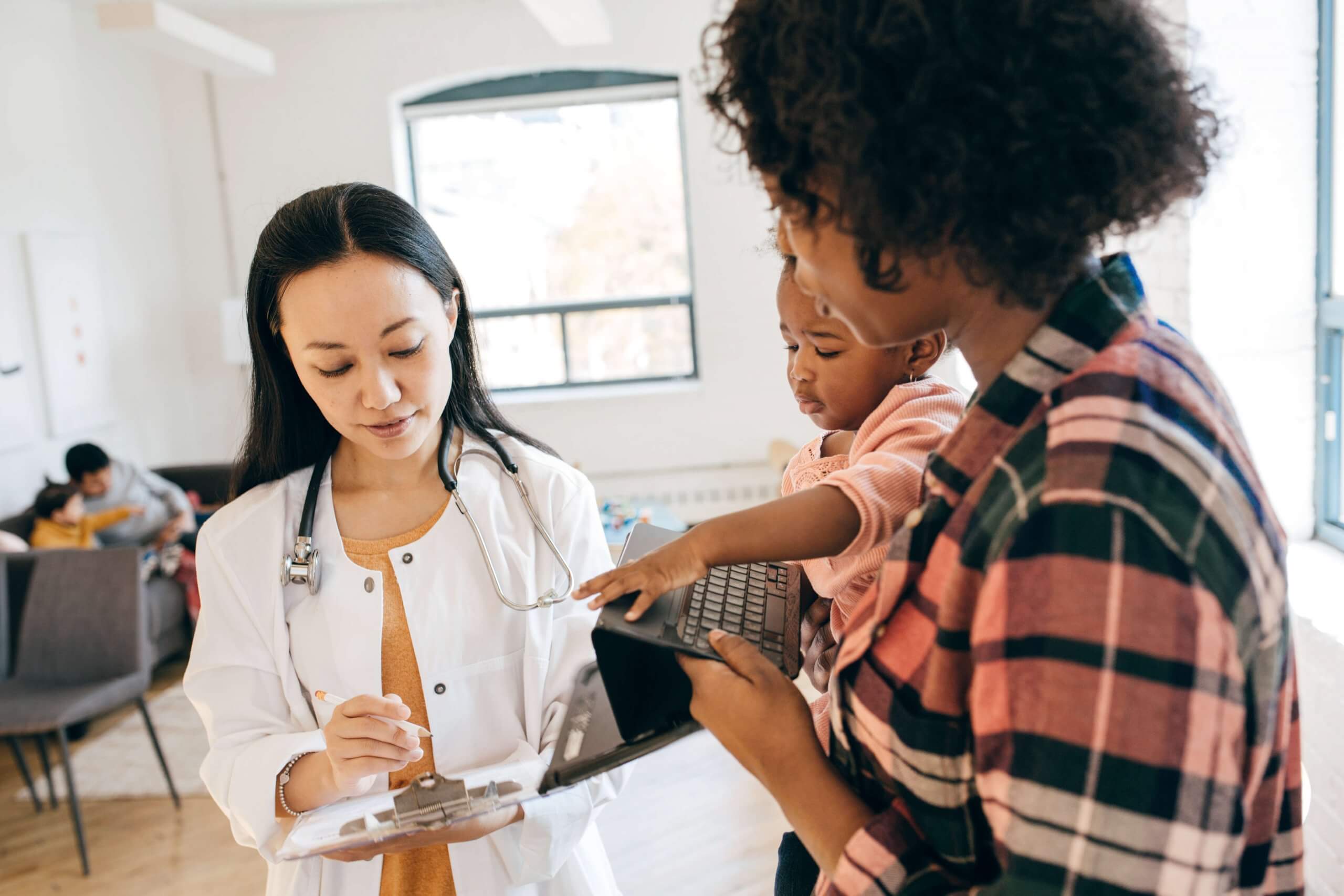
Finding a diagnosis for rare diseases is often a race against time. QIAGEN Digital Insights is helping provide answers where none were available before.


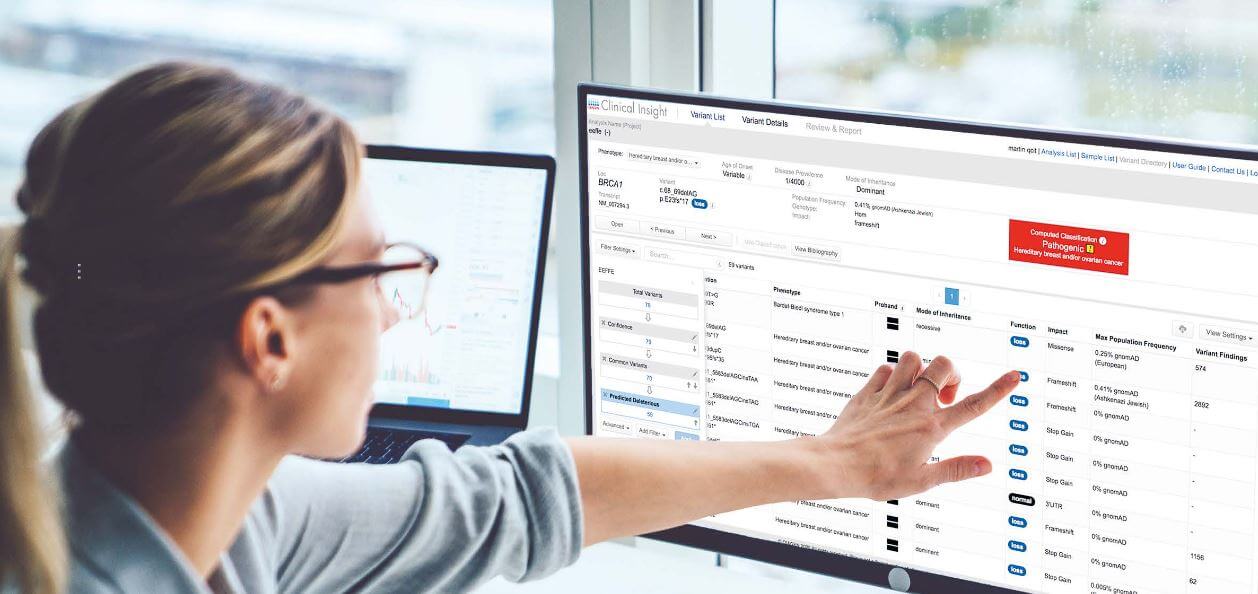
Whole-exome sequencing (WES) has shown an unprecedented success rate in the identification of disease-causing genetic variants. On average, 25 to 32 percent of patients who undergo clinical exome testing receive a diagnosis [1]. WES testing examines all the protein-coding regions in the genome (exons) simultaneously. Approximately 85% of all disease-causing mutations are located within the exons [2]. By casting a wider net, WES increases the chance of reaching an accurate diagnosis.
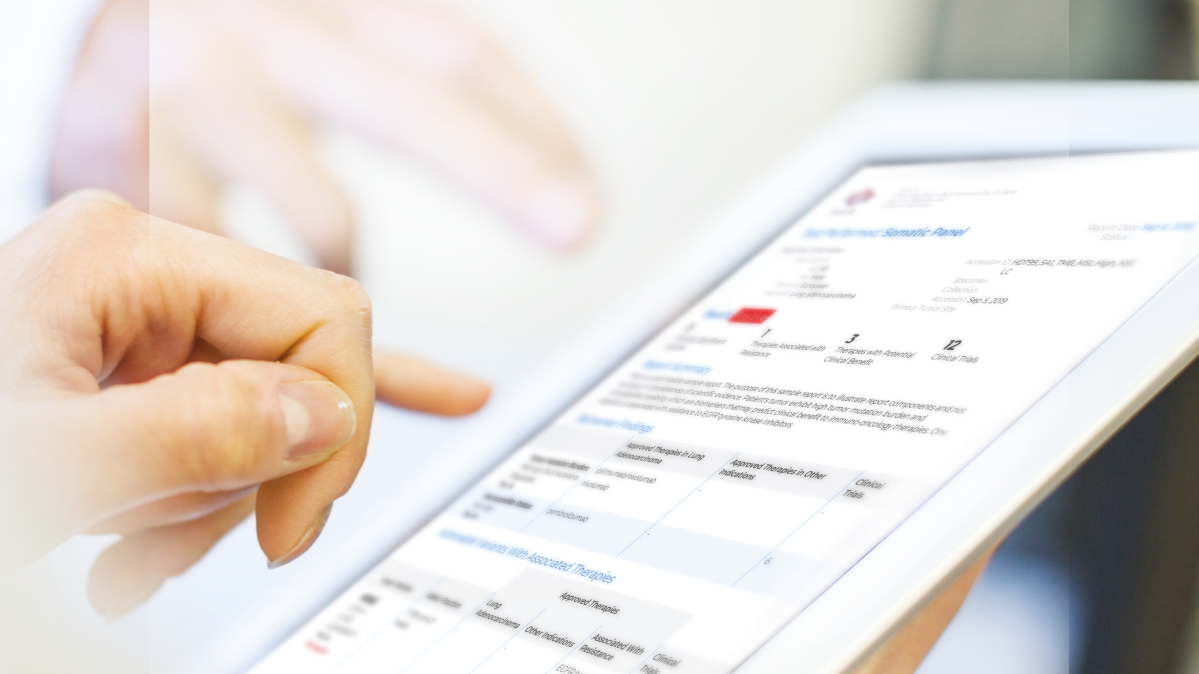
Dr. Atil Bisgin at Çukurova University Hospital in Adana, Turkey manages one of the largest databases for rare hereditary diseases in the world. Using QIAGEN Clinical Insight (QCI) Interpret, Dr. Bisgin is rapidly identifying causative mutations in rare diseases.


Learn more about QIAGEN's QIAseq Human Exome Kits.