


















New content, new projects, External Scripts improvements and more!
Recently-added Lands in OncoLand
OncoLand has added several new Lands over recent releases, be sure to check them out! If you do not see these Lands in your OncoLand collection, please contact your QIAGEN OmicSoft Server administrator to add the Lands to your server.
Body Maps
GTEx_B37 has 8711 new RNA-seq samples, and 16,964 total RNA-seq samples. GTEx_B38 is scheduled to be updated to GTEx V8 with 2020R2.
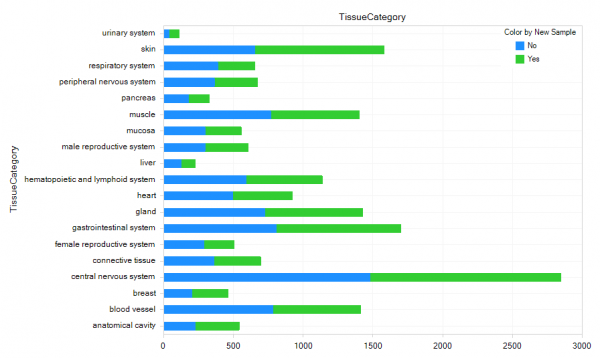
New projects in OncoLand 2020R1
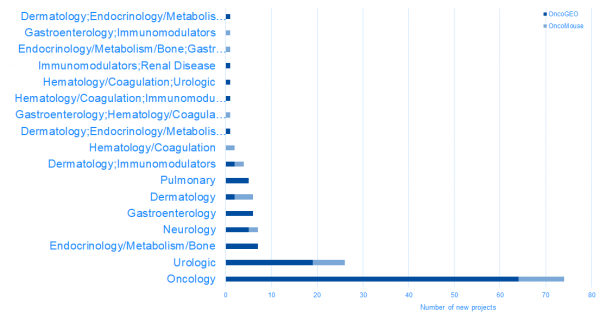
New projects in DiseaseLand 2020R1
HumanDisease project highlights:
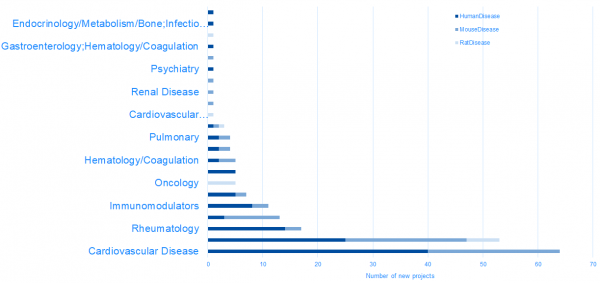
RatDisease project highlights:
MouseHumanDisease project highlights:
Array Suite is now QIAGEN OmicSoft Suite
This is purely a name change to reflect the wide variety of Omics data supported by QIAGEN OmicSoft.
OmicSoft Studio=Array Studio. OmicSoft Server=Array Server. OmicSoft Viewer=Array Viewer.<

Improved External Scripts with support for Docker technology and cloud analysis
OmicSoft Suite now supports External Scripts on AWS Cloud and can run analyses on Docker images. See some examples here.
These new capabilities substantially expand the options for OmicSoft Suite as an ‘omics data and analysis hub, allowing advanced users who would like to run third-party bioinformatics tools to do so from OmicSoft Suite, and even build pipelines to analyze data and import into OmicSoft projects. Talk with your account manager to learn more about some of the possibilities.
Updates to other OmicSoft Suite functions
Now you can download FASTQ files up to 100GB from the Short Read Archive. Previously, downloading FASTQ data from the NCBI Short Read Archive (SRA) database supported files only up to 20 GB.
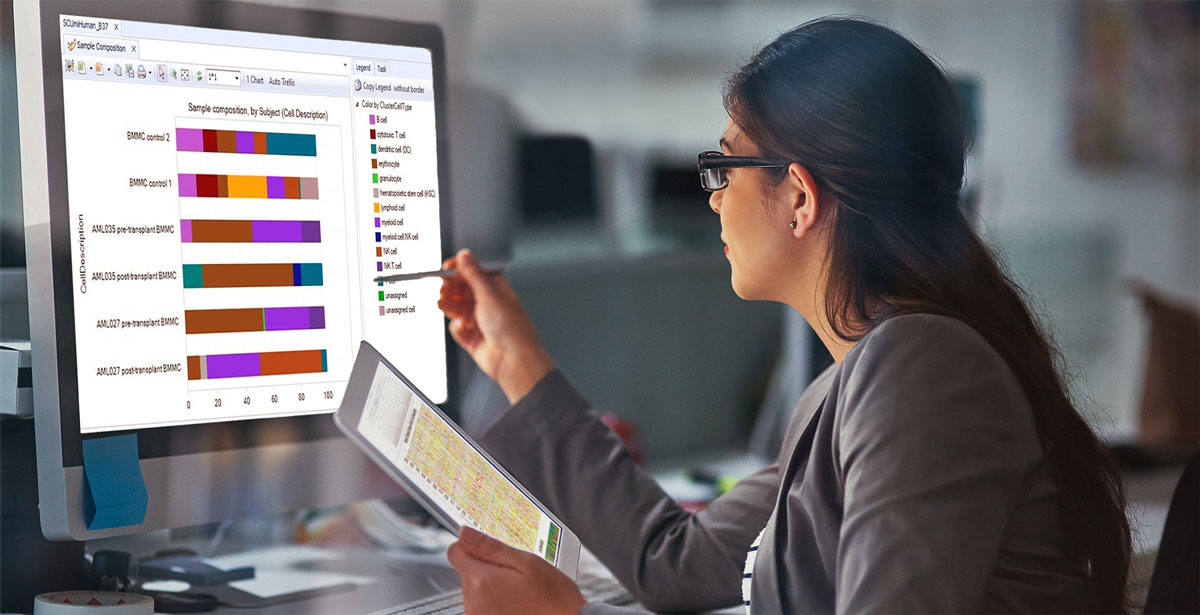
The “Single Cell Quantification” function now supports antisense strand reads (commonly generated from 5′ chemistry) in addition to sense strand reads (3′ chemistry), increasing the flexibility to support new workflows.
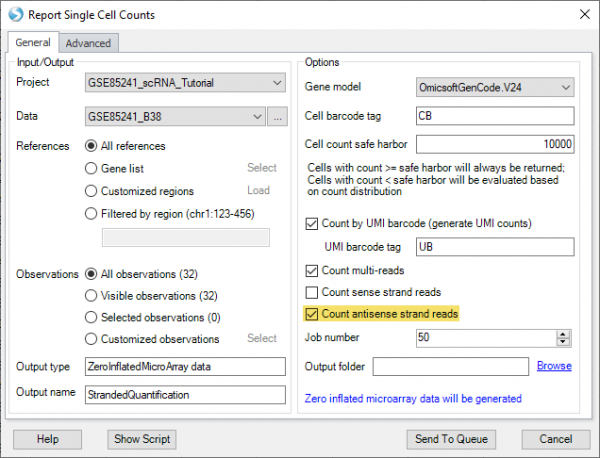
In “Map RNA-seq reads to genome“, there is a new option to pair input files in the order they were submitted, instead of pre-sorting the files by name. This is useful in exceptional situations, such as when data for the same sample are stored across multiple files in multiple directories, and the file names are identical between directories.
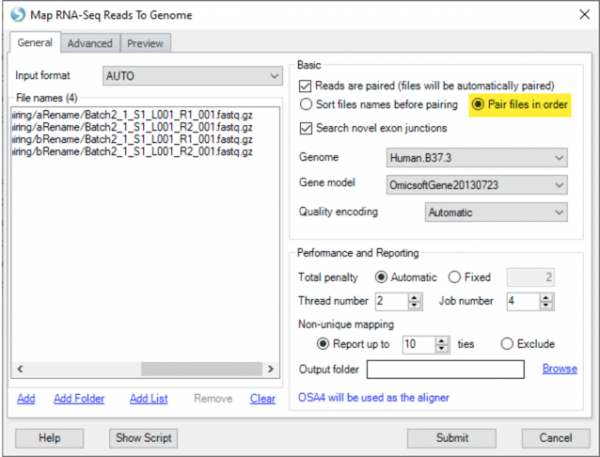
For example, if your data were run across multiple lanes, and the output files for Read1 are saved as “Batch2_1_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz” in multiple directories (each directory holding data from one lane), you can ensure proper file pairing by specifying the order with “Add List” or during sample registration, and by selecting “pair files in order” when specifying alignment options.

Our recent virtual QIAGEN IPA/OmicSoft User Group Meetings that took place in April and May were both a great success. We hope you were able to join us! Review the recordings here.
Stay tuned for more QIAGEN IPA/OmicSoft User Group Meetings taking place later this year.
Learn more about the QIAGEN OmicSoft portfolio here.