

















The incidence of cancer has been growing in Japan, with about 1 million patients diagnosed each year and one of every two people now developing cancer during their lifetimes. Genomic insights often aid in clinical decision-making by revealing somatic changes, which may be caused by lifestyle factors, such as smoking or diet, or inherited (germline) variations – either of which can influence the efficacy of oncology drugs. Genomic profiling may help physicians match therapies to the precise combination of genetic variants for this or other cancers

In 2018, the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics (C-CAT) was established by the National Cancer Center of Japan to make a difference by offering cancer patients in Japan the most advanced care available, using genomic medicine to optimize and personalize strategies for treatment and prevention based on somatic and germline profiles.

The National Cancer Center of Japan uses the QIAGEN Clinical Insights (QCI) platform including expert-curated evidence knowledge bases, bioinformatics software, and data center infrastructure, to support the C-CAT’s molecular profiling services for core hospitals of the country’s cancer genomic medicine program. QIAGEN has established an in-country data center in Tokyo, compliant with Japanese data security and privacy regulations, to support this national program.

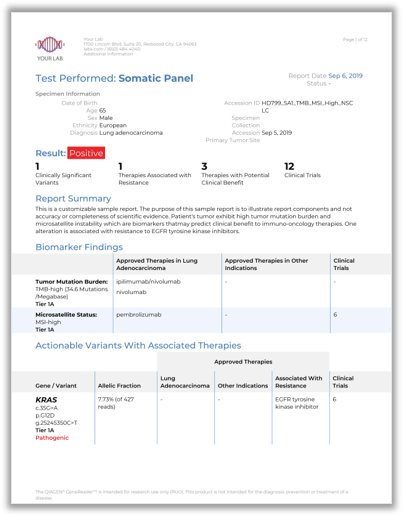
QCI is a cloud-based clinical decision support software platform used to generate actionable insights from next-generation sequencing (NGS) data.
QCI leverages QIAGEN’s expert manually curated evidence knowledge base that includes more than 20 million biomedical findings and is the world’s largest commercial database of curated evidence data on somatic and inherited genetic variants. QCI minimizes the complexity and cost of determining the significance of NGS data and automates guidelines for clinical actionability from leading oncology and pathology organizations.