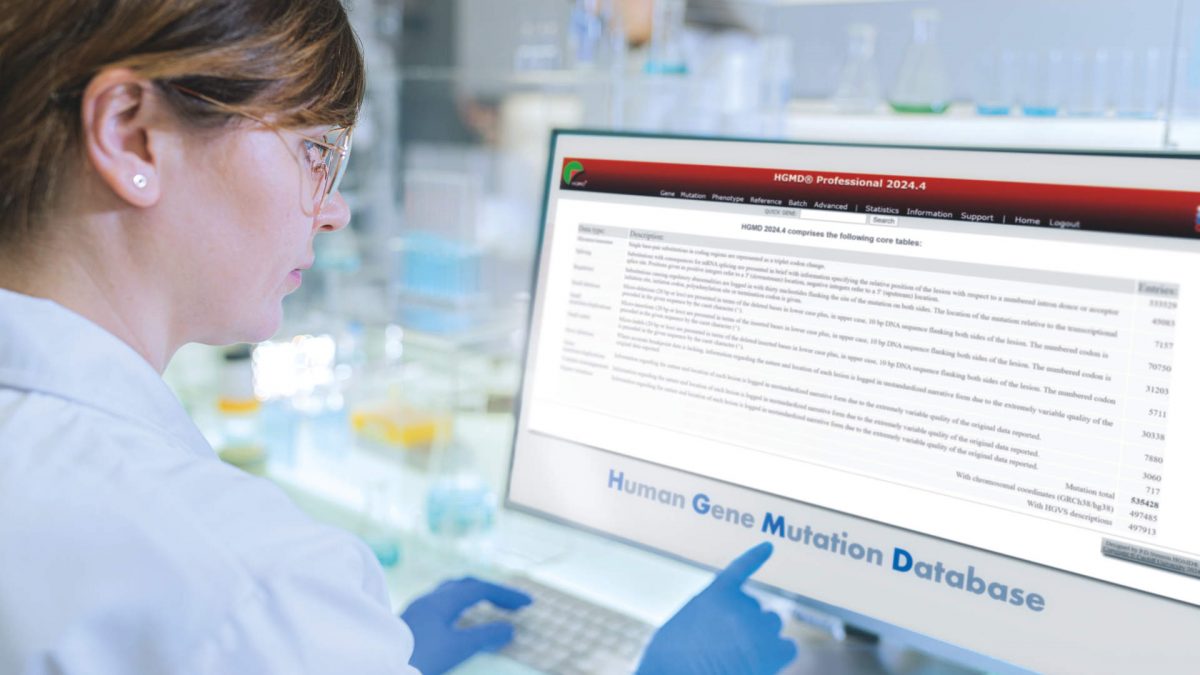



















The HGMD Professional 2024.4 release sees 7618 new entries on inherited disease-associated variants, including 57 new genes, for a total of 535,428 comprehensive variant reports. In line with our standard of excellence, we’ve also added new primary and secondary literature to 15,258 mutation entries.
The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) is a unique database that provides clinical labs with the latest and most reliable insights into disease-associated variants. The database was founded by the Institute of Medical Genetics at Cardiff University in 1996 with the goal of facilitating the scientific study of mutational mechanisms in human genes underlying inherited disease. However, over the last 25 years, it has acquired a much broader utility, as it has become the central unified repository for disease-related genetic variation in the germline.
Today, two versions of the database are offered: HGMD (a free, publicly available database) and HGMD Professional (a stand-alone web application, made available under license exclusively from QIAGEN). HGMD Professional is the version of the database most appropriate for clinical applications, as the professional version is three years ahead of the public version in terms of content. It’s important to understand that the mutation data in HGMD Professional is made freely available via the public version of HGMD three years after initial inclusion. Therefore, if your lab needs access to up-to-date mutation data, HGMD Professional provides content from the latest publications.
HGMD Professional is maintained and manually curated by a team of variant scientists and bioinformaticians at Cardiff University. These expert curators, each certified and trained in germline variant curation with an average of more than 12 years experience in curation, screen peer-reviewed biomedical literature on an ongoing basis through a combination of automated and manual processes. Currently, HGMD Professional contains data derived from over 72,000 manuscripts published in more than 3,100 different journals.
The number of disease-associated germline mutations published per year has more than doubled in the past decade (Figure 1). As rare and novel genetic mutations continue to be uncovered, HGMD Professional ensures your lab has access to the latest scientific evidence needed for timely interpretations of NGS data.
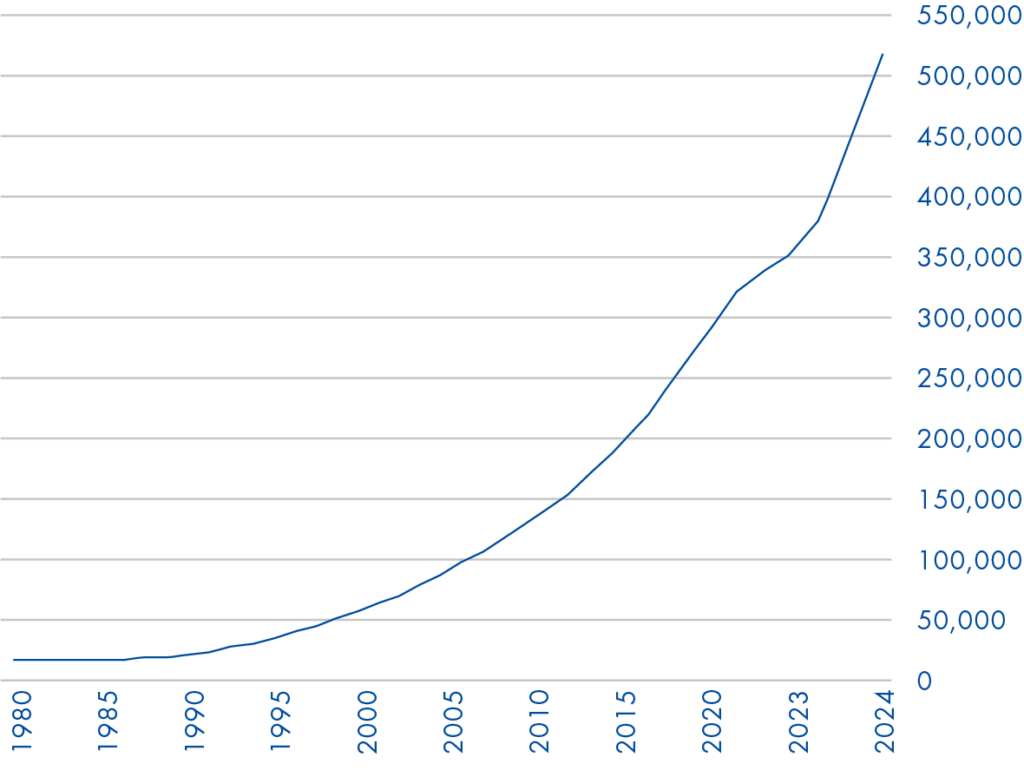
Figure 1. Gene mutation entries in HGMD Professional 2024.4. The number of inherited disease-associated germline mutations published per year has more than doubled since 2015.
In the new HGMD Professional 2024.4 release, more than 7500 mutation entries have been added to the database:
→ View the complete HGMD Professional 2024.4 data updates here.