
















In Genetics in Medicine, a study entitled, “Comparison of literature mining tools for variant classification: Through the lens of 50 RYR1 variants” was published by Wermers et al. of the Center for Precision Health Research at the NIH. Recognizing the importance of accessing relevant literature that informs the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) criteria for classifying variant pathogenicity, investigators set out to determine the efficacy of four literature mining tools in the retrieval of publications to classify 50 RYR1-related malignant hyperthermia susceptibility genes. The four tools included QIAGEN’s HGMD Professional, Genomenon® Mastermind®, ClinVar, and LitVar2.
*Findings are from a peer-reviewed study, Wermers et al. Genet Med. 2024;26(7):101161. Mastermind is a product from Genomenon with no affiliation to QIAGEN. All data taken directly from the published study.
The content of each reference returned by all four literature mining tools was analyzed to determine if the publication was a primary or secondary source:
Researchers calculated sensitivity and precision for the four literature mining tools with reference to the number of papers we deemed relevant for ACMG/AMP/ClinGen classifications.
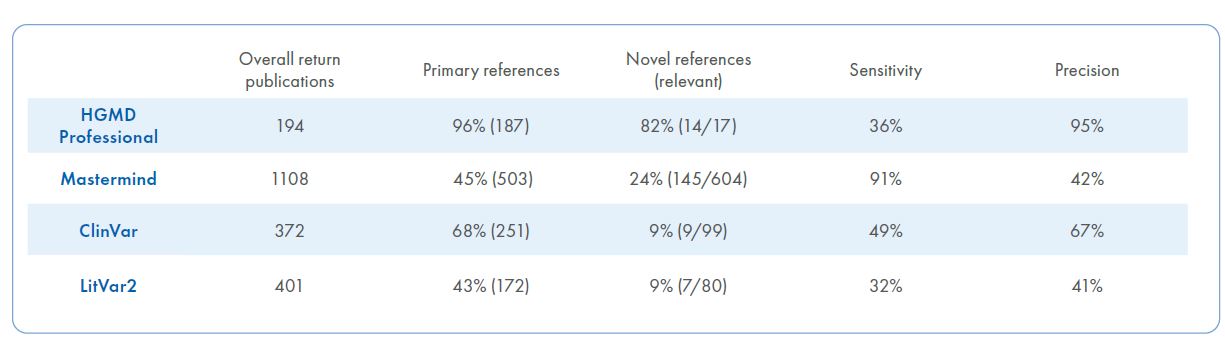
Table 1. Metrics for the four literature mining tools. Data is presented for each tool, including overall number of publications returned, number of primary references, number of novel references, sensitivity and precision.
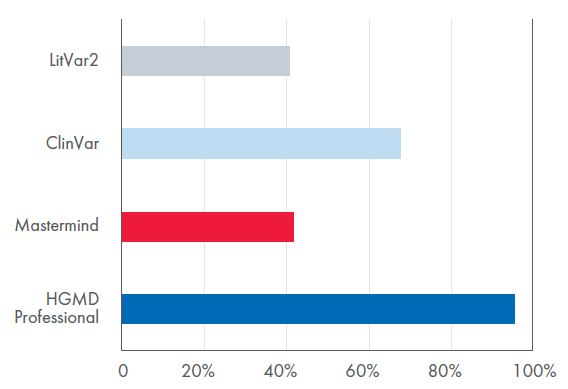
Figure 1. Comparison of precision between the four tools. HGMD Professional had the highest precision at 95%. In comparison, Mastermind® had a precision rating of 45%.
Don't just take our word for it. Download an expert white paper providing an overview of the study, with details on the methods, additional data, and why the NIH trusts HGMD Professional over other commercial and publically available literature mining tools.
Explore, search and test HGMD Professional for free. To demonstrate the quality, flexibility, and superiority of HGMD Professional, QIAGEN Digital Insights offers complimentary, no-obligation trials of the leading database. Start your free trial today!


