Conquer the genetic complexity of inherited cardiac arrhythmias with database and software solutions for analyzing and interpreting large NGS multigene panels
Individuals carrying a pathogenic variant for a dominantly inherited arrhythmia have a 50% likelihood of passing the variant on to their children, placing them at higher risk of developing the potentially life-threatening condition (1).
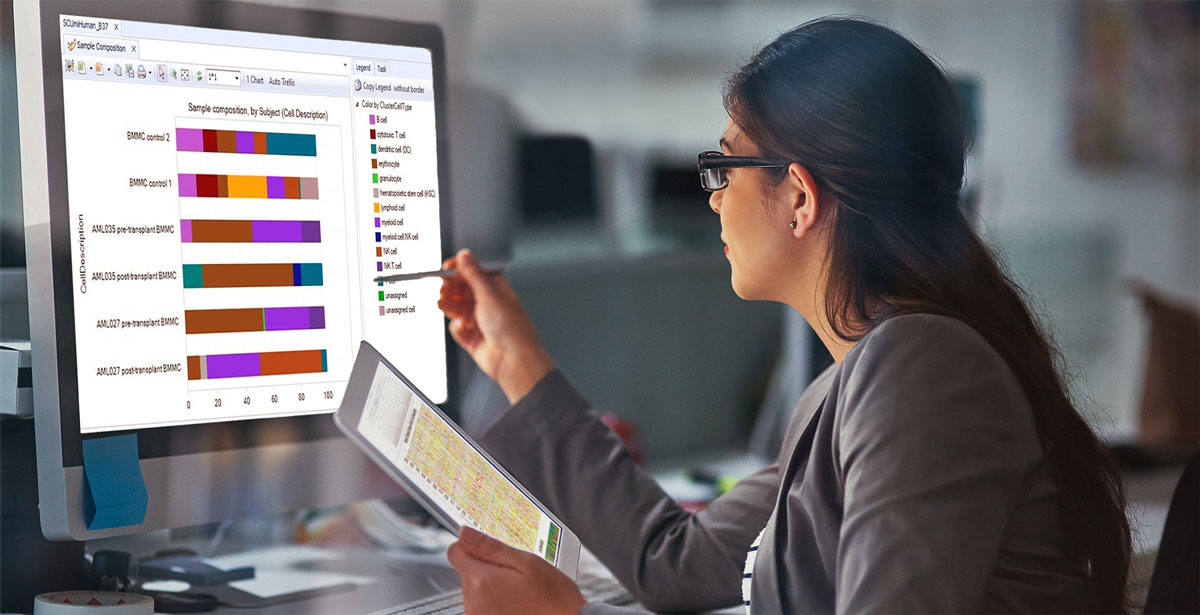
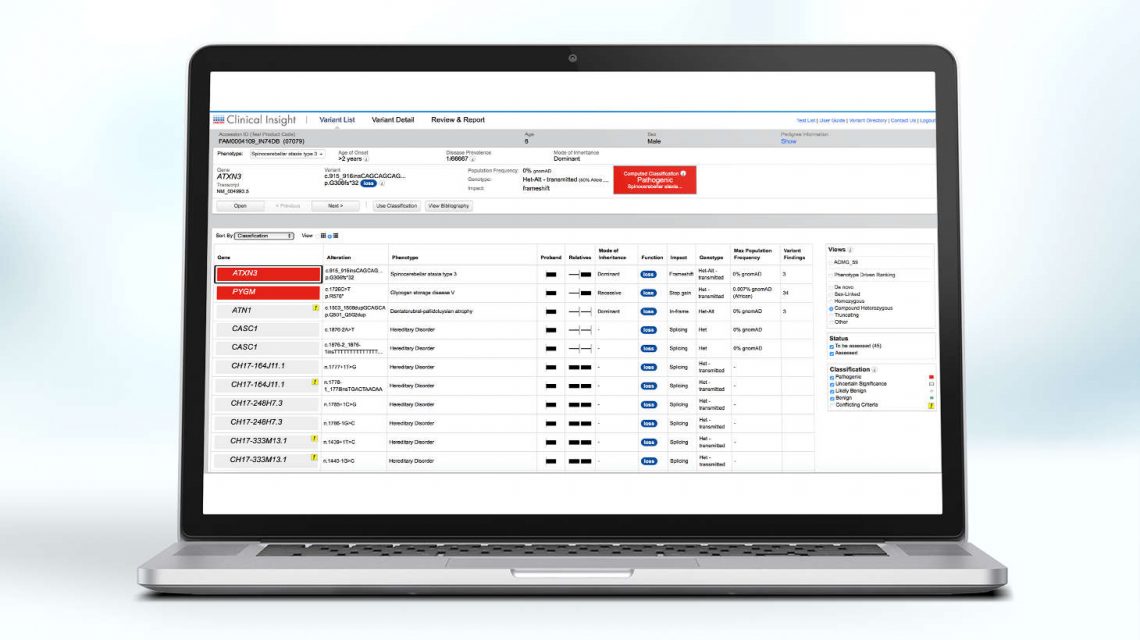
Today, there are a several commercially available sequencing options for genetic testing of inherited arrhythmias, ranging from targeted panels (5-20 genes) to broad pan-arrhythmia panels (170+ genes) and whole exome sequencing (20,000+ genes). While more comprehensive tests increase the sensitivity of variant detection, they also increase the detection of variants of unknown clinical significance, enhancing the complexity of interpretation.
There are several types of inherited arrhythmic disorders. The most common types include:
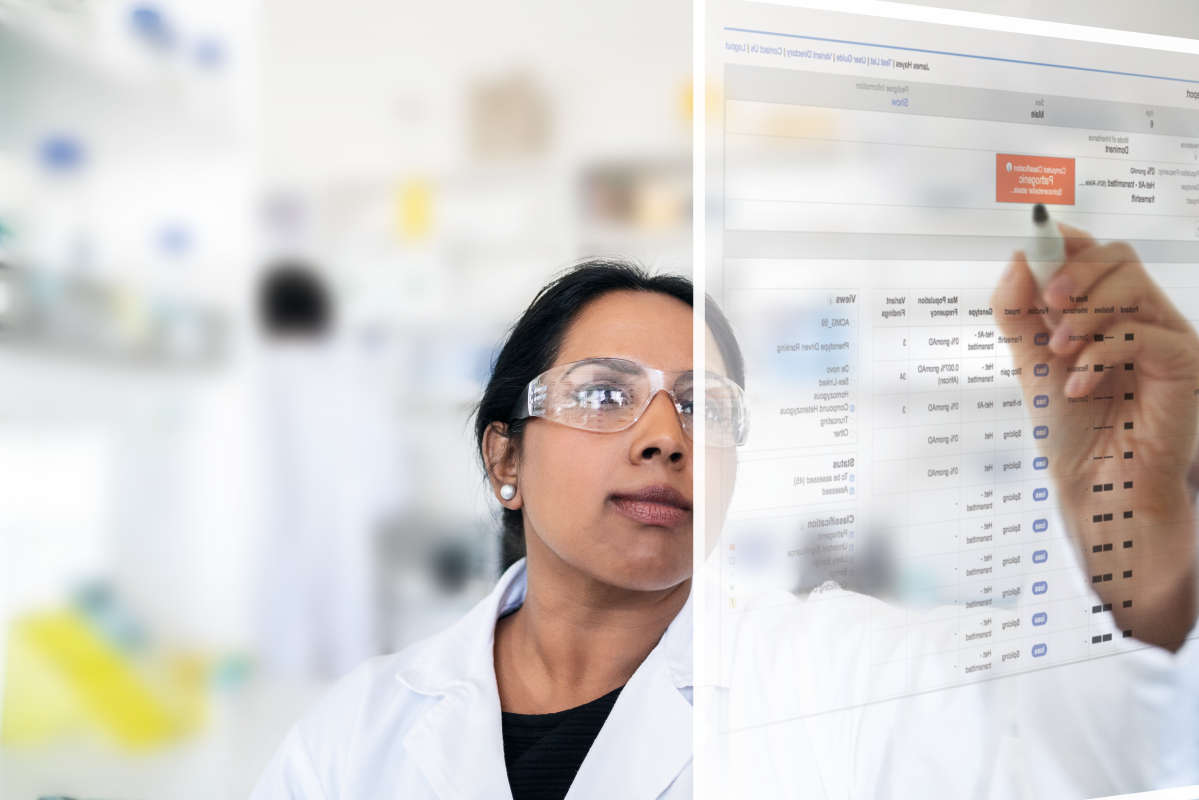
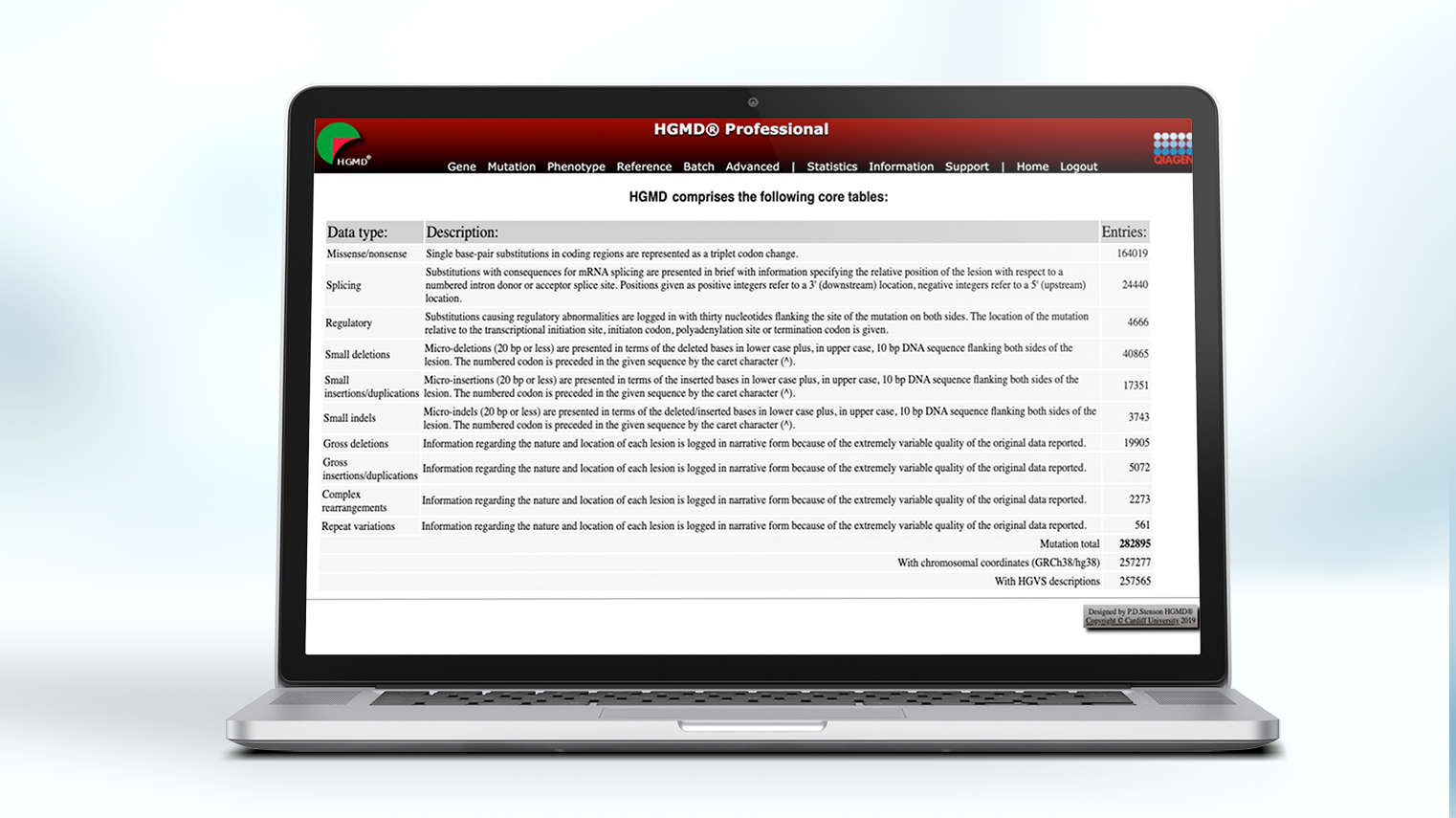
The content core of QIAGEN's clinical NGS variant interpretation and reporting solutions, the QIAGEN Knowledge Base (QKB) is unrivalled in breadth, depth, and accuracy, ensuring labs have access to the evidence, peer-reviewed literature, guidelines, drug labels, and clinical trial registries needed to interpret every variant with precision and confidence.
Built over 20 years and encompasses over 40 public and proprietary databases
Maintained by hundreds of certified MD- and PhD-level expert curators who enter more than 5,000 new findings each day
Contains the latest evidence from peer-reviewed papers, clinical and functional studies, on- and off-label drugs, and professional guidelines, such as NCCN, AMP/ASCO/CAP and the World Health Organization (WHO)
Updates list of recruiting clinical trials each week