

















We are pleased to announce that the Winter 2023 Release of QCI Interpret Translational, QIAGEN’s web-based software application for the annotation, classification, and research of somatic and germline variants, is now available.
Expanding on the software’s current capabilities, the QCI Interpret Translational Winter 2023 Release brings new variant classification and assessment tools, greater customization, and even more variant content for prevalent hereditary diseases for faster, more informed variant analysis.
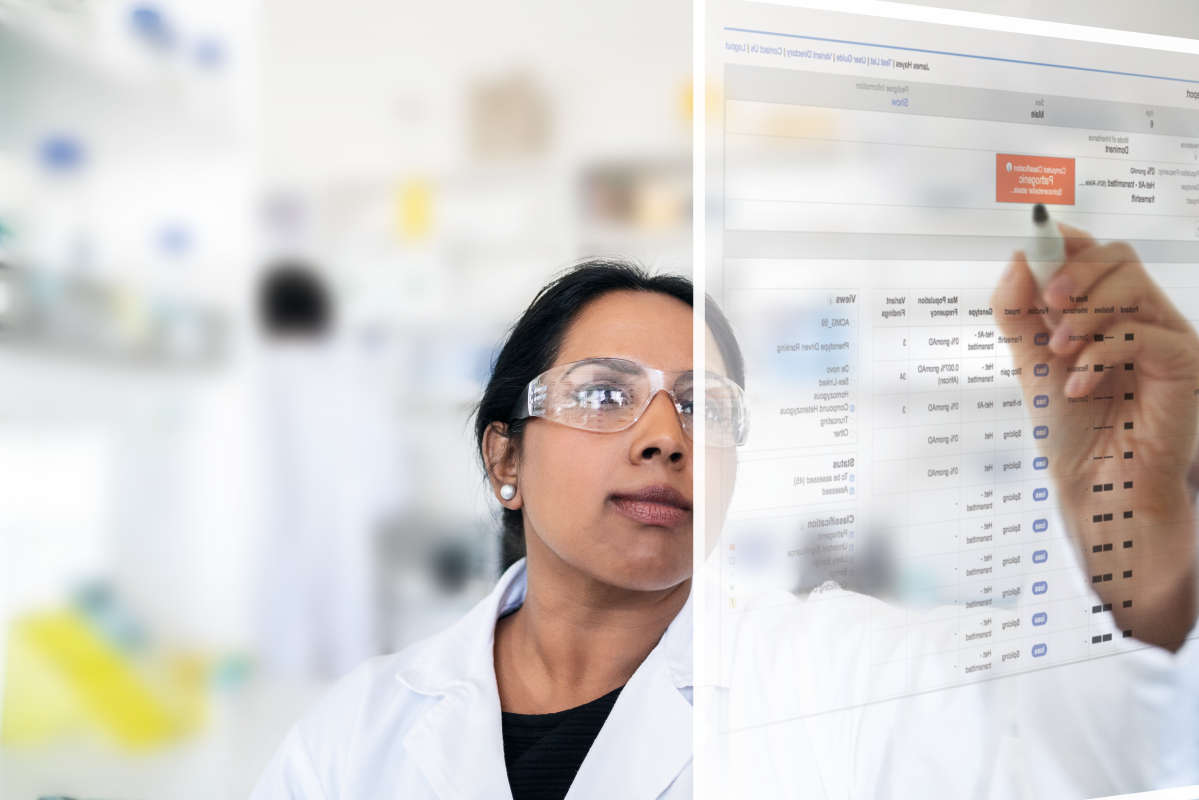
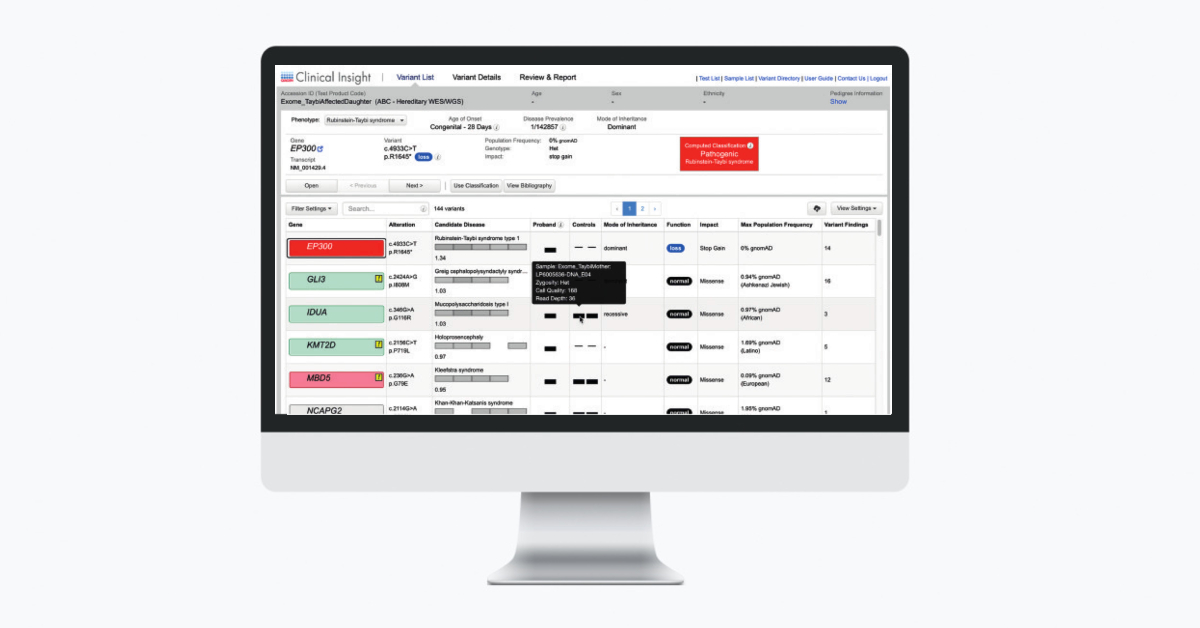
QCI Interpret Translational now offers a new optional Triage Mode inline assessment tool to accelerate variant review workflows. The Triage Mode can be toggled on and off (Figure 1).

For novel unassessed variants, the Assessment, Actionability (somatic workflow only), and the Reportability values match the Computed Classification. Users can then add assessment notes (Figure 2). This new feature is intended to help high volume laboratories quickly assess and triage variants.

QCI Interpret Translational’s literature coverage of genes, involved and associated with disease(s), strongly differentiates QCI Interpret Translational from other NGS variant assessment software by providing a fully certified and manually curated bibliography of approximately 1,000 genes with continuous expansion.
In the QCI Interpret Translational Winter 2023 Release, the bibliography coverage is enhanced and expanded with a focus on genes that are routinely tested and proposed for carrier screening by the latest ACMG practice resource (Genetics in Medicine (2021) 23:1793–1806; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-021-01203-z).
Specifically, the bibliography coverage was fully certified and manually curated for Tier 3 genes with continued curation of Tier 4 genes, to provide a comprehensive and complete carrier screening interpretation workflow based on the latest ACMG recommendations summarized below:
In QCI Interpret Translational, a new ClinVar column displays the assessment (P, LP, VUS, LB, B) and number of ClinVar submitters as pulled from the QIAGEN Knowledge Base. A hyperlink takes the user to the respective ClinVar VCV page (phenotype agnostic) (Figure 3).
Pathogenic (P), Likely Pathogenic (LP), VUS, Likely Benign (LB), and Benign (B) interpretations sent to ClinVar are tallied. The hyperlink takes the user to the NCBI variant specific page for additional detail.
For the complete QCI Interpret Translational Winter 2023 Release Notes, please contact your QIAGEN Digital Insights account representative or email our support team at ts-bioinformatics@qiagen.com.
QCI Interpret Translational is a web-based software application for the annotation, classification, and research of variants from next generation sequencing (NGS) data in genomic laboratories. Using augmented molecular intelligence and expertly curated content from the QIAGEN Knowledge Base, QCI Interpret Translational uses evidence-based approaches to automatically compute pathogenicity classifications (Pathogenic to Benign) and actionability classifications (Tier 1 to 4) for each alteration according to the 2015 professional guidelines from the American College of Medical Genetics and Association for Molecular Pathology (ACMG/AMP) [1] and the 2017 guideline from the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists (AMP/ASCO/CAP) [2], respectively.
Pathogenicity and actionability classifications in QCI Interpret Translational are accompanied by clear visibility into the criteria and evidence supporting the classifications. This workflow starts with a variant call format (VCF) file, so it is compatible with the output from any NGS platform. The final analysis is sample-specific and includes candidate causal variants, their deep annotations, interpretations, and references specified throughout the assessment process. The assessment process also has customized automation allowing for even more streamlined variant research workflows.
QCI Interpret Translational helps research labs: