Genome and exome sequencing is transforming cancer diagnostics and care. In the first installment of our Advancing Clinical NGS series, learn how molecular diagnostic labs can overcome the complexity of implementing bioinformatics workflows for cancer genome and exome sequencing.
How can whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and whole-exome sequencing (WES) be integrated into health care systems to replace the standard of care for oncology? These next-generation comprehensive precision diagnostic tests have the potential to become the best practice for oncology molecular testing in health care systems around the world. However, implementation and wide-scale adoption of the best-in-class testing is lacking.
In this blog, we discuss how clinical diagnostic labs can overcome challenges of implementing WGS and WES for cancer and show how QCI Interpret for Oncology, the industry’s most advanced FASTQ to final report solution for precision oncology NGS testing, can be used to analyze and interpret WGS panels for cancer with speed and precision.
The triple challenge of cancer genome and exome sequencing
- Cost barrier: One of the primary obstacles to widespread adoption of cancer genome and exome sequencing is the cost. While the cost has significantly decreased over the years, it can still be a barrier to widespread implementation, especially in resource-limited settings. As a result, clinical labs implementing WGS and WES for cancer must adopt bioinformatic solutions that can improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Data deluge: Genome and exome sequencing generates vast amounts of data, presenting a formidable challenge for storage, analysis, and interpretation. The sheer volume of genetic information requires sophisticated computational tools and expertise in bioinformatics to identify clinically relevant mutations amidst the genomic noise. As sequencing technologies continue to advance, managing and analyzing this deluge of data will remain a critical challenge.
- Variant interpretation: Identifying the genetic mutations driving cancer and distinguishing between driver mutations that directly contribute to tumorigenesis and passenger mutations that are incidental remains a daunting task. Deciphering the functional significance of genetic alterations requires a deep understanding of cancer biology and genetic pathways. Moreover, the interpretation of genomic data must be nuanced, taking into account tumor heterogeneity, clonal evolution, and the dynamic nature of cancer genomes.
Cancer genome and exome interpretation with QCI Interpret
QCI Interpret for Oncology is an end-to-end solution for NGS data analysis, interpretation, and reporting that helps clinical diagnostic labs scale the process of FASTQ to final report. Comprised of two integrated software applications with an additional in-software option to send rare or novel variants to QIAGEN’s on-demand variant interpretation service, QCI Interpret for Oncology alleviates the complexities of regulating in-house bioinformatics pipelines to reduce turnaround time, simplify variant interpretation, and support confident decisions. Below, we provide a few examples of unique features in QCI Interpret for Oncology that support cancer genome and exome interpretation.
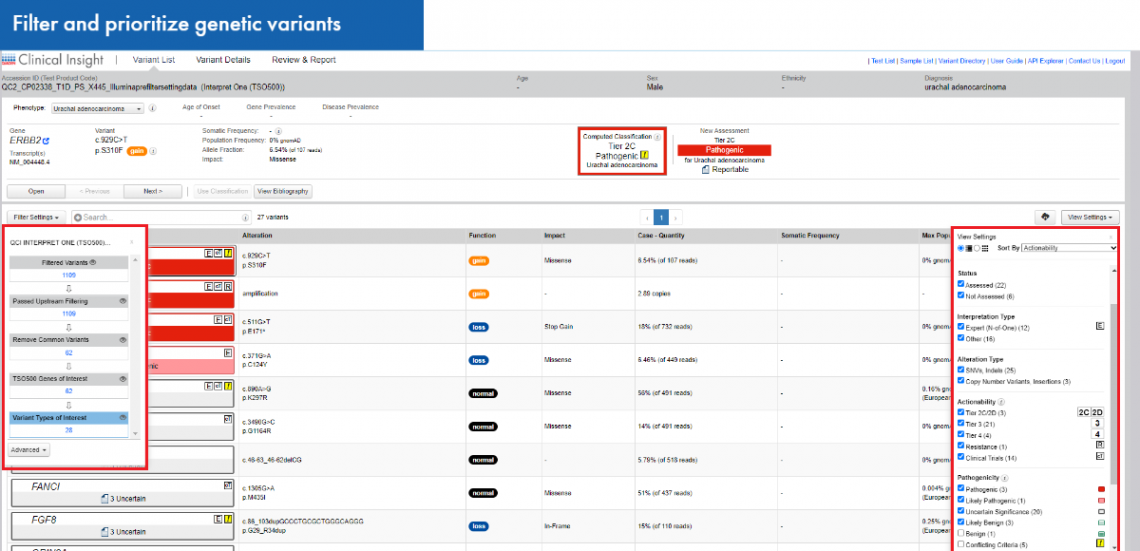
Use QCI Interpret for Oncology to group, filter, and prioritize genetic variants from the variant lists. Find actionable mutations in driver genes and match driver alterations with specific drugs allowing personalized therapeutic management. Sort your variants by interpretation type, alteration type, and clinical actionability in search for those that could be used as prognostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
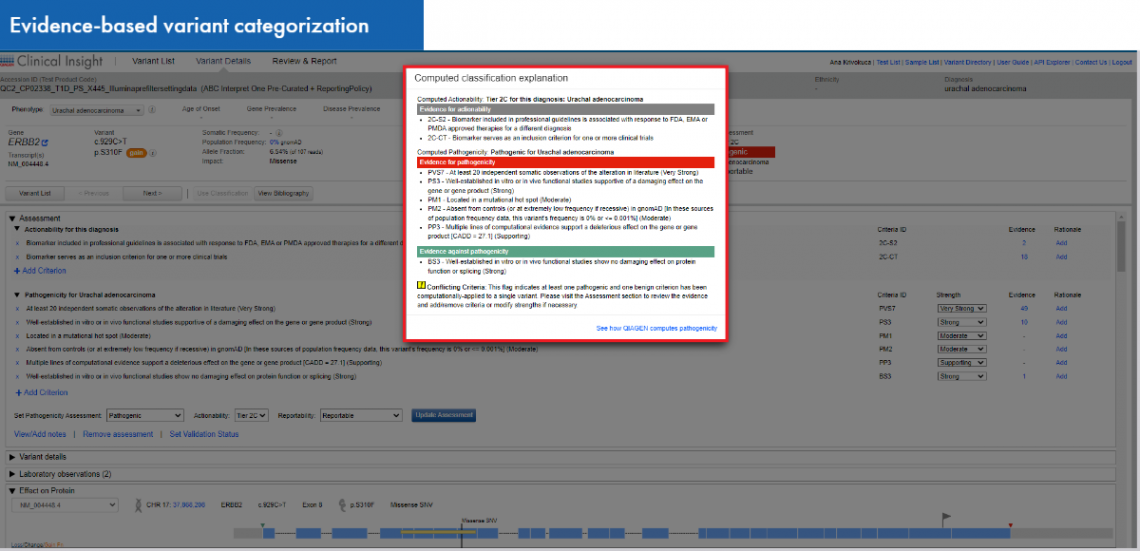
Clinical cases are deeply curated to gather specific evidence for automated computation of an AMP-recommended classification into 4 categories: Tier 1- variants of strong clinical significance (Level of evidence A and B), Tier 2- Variants of potential clinical significance (Level of evidence C and D), Tier 3 –Variants of unknown clinical significance, and Tier 4- Benign or Likely benign variants. For each computed classification the criteria engaged are displayed along with the supporting evidence.
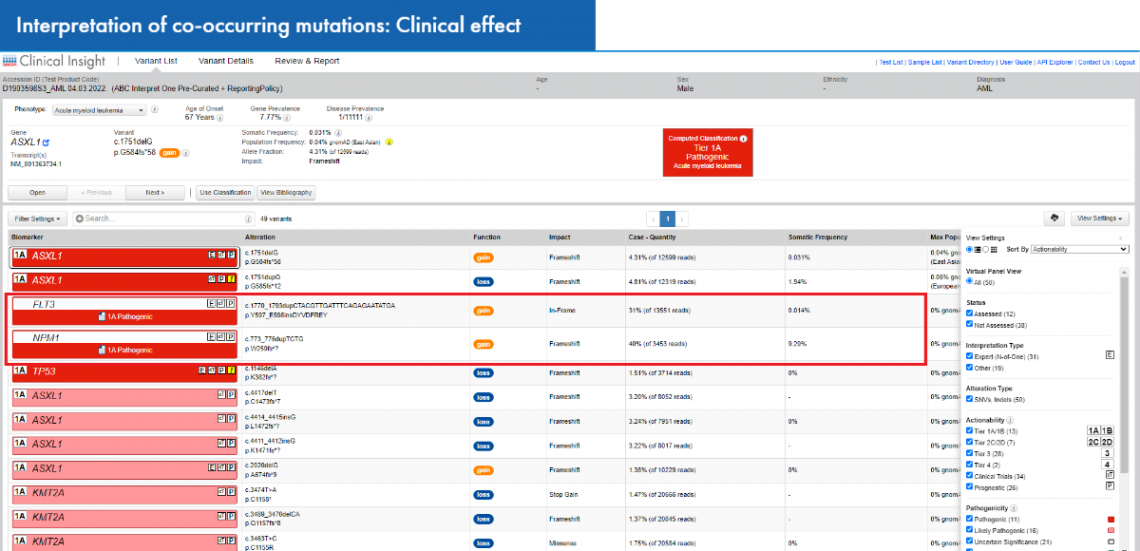
QCI Interpret for Oncology identifies and lists co-occurring variants in each clinical sample, providing evidence on the clinical effect with reference to relevant guidelines. The software allows you to filter variants according to genes in which actionable mutations are detected and to visualize the co-mutations that exist in the sample. Users also receive an expert explanation on the clinical effect of the co-occurring mutations with reference to clinical guidelines.
Danish National Genome Center selects QCI Interpret for variant interpretation in oncology genome sequencing
The QCI Interpret solution was chosen by the Danish National Genome Center to provide interpretation of oncology results generated from whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data. The initiative is part of a larger personalized medicine strategy that aims to provide WGS as the standard-of-care for relevant patient groups throughout Denmark.
Denmark is one of the first countries in the world to implement WGS as standard-of-care for oncology at this scale. Through the adoption of QCI Interpret, the country aims to gain sufficient genetic data to truly utilize the power of genomics in personalized medicine to improve outcomes for patients through better cancer diagnosis and treatment decisions.
The Danish National Genome Center selected QCI Interpret to streamline and accelerate the interpretation and reporting process. QCI Interpret delivers evidence-based variant interpretation and reporting and adheres to the highest level of data security and privacy. This enables flexibility at distributed testing sites throughout the country that use different next-generation sequencing (NGS) instruments. In addition, the platform is an agnostic solution, so it can be easily integrated with any pipeline to enable users to go from variant calls to final report within minutes.
Deliver clear and confident precision oncology reports
QCI Interpret for Oncology is an end-to-end solution for NGS data analysis, interpretation, and reporting that helps clinical diagnostic labs scale the process of FASTQ to final report. Comprised of two integrated software applications with an addtional in-software option to send rare or novel variants to QIAGEN’s on-demand variant interpreation service, QCI Interpret for Oncology alleviates the complexities of regulating in-house bioinformatics pipelines to reduce turnaround time, simplify variant interpretation, and support confident decisions.

