Latest improvements for IPA
What’s new in the QIAGEN® Ingenuity Pathway Analysis Spring Release (2024)
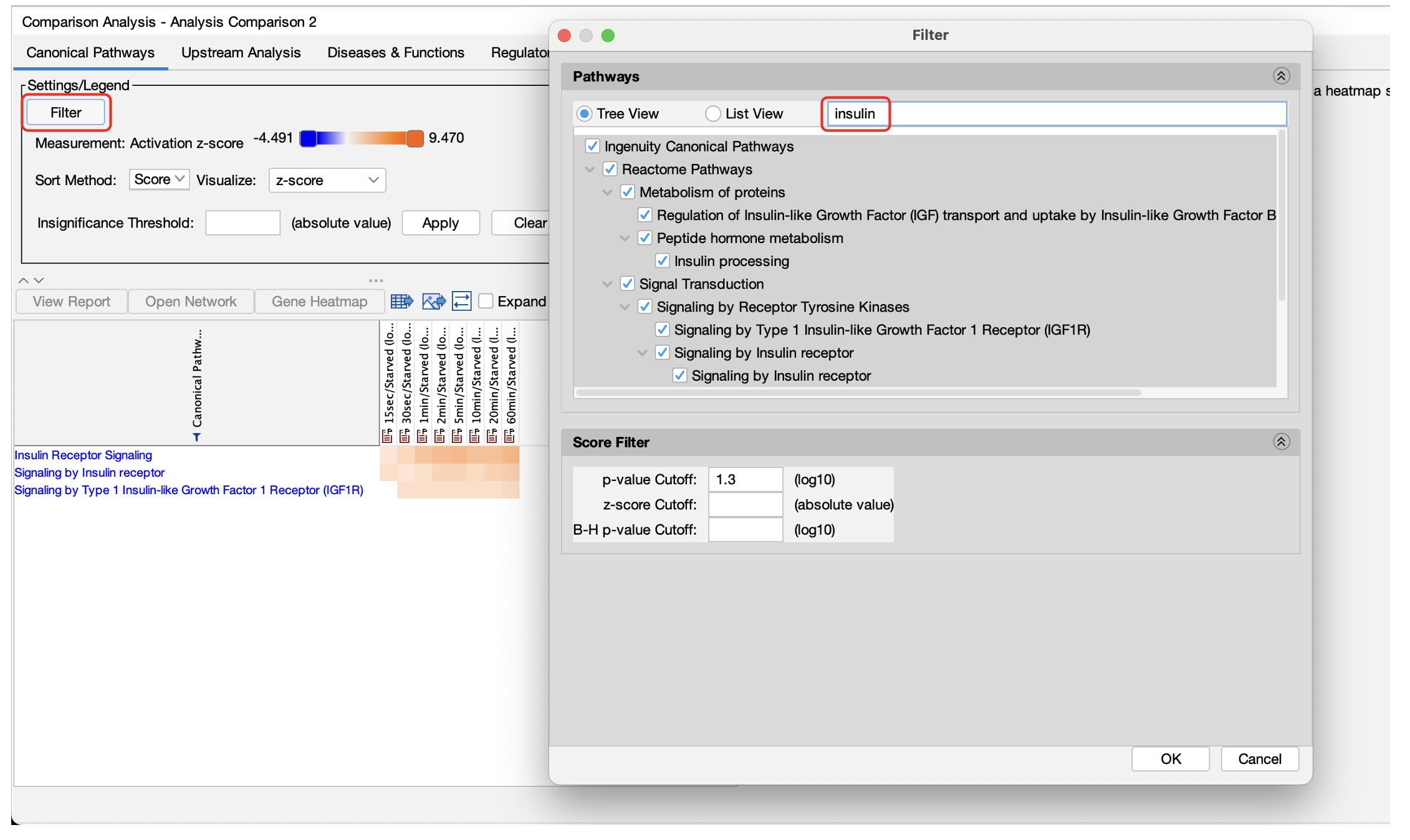
Search and filter Canonical Pathways by name in Comparison Analysis heatmaps
Quickly select a subset of Canonical Pathways for heatmap display by searching for words in the pathway names. This enables you to create the perfect heatmap for image export for presentation or publication.
Figure 1. Search and filter by pathway names in Comparison Analysis. Simply type words from the pathway name(s) to focus the heatmap on pathways of interest.
Content updates
Canonical Pathways updates
New Ingenuity Signaling Pathways
- Cohesin Chromatin Regulation Pathway
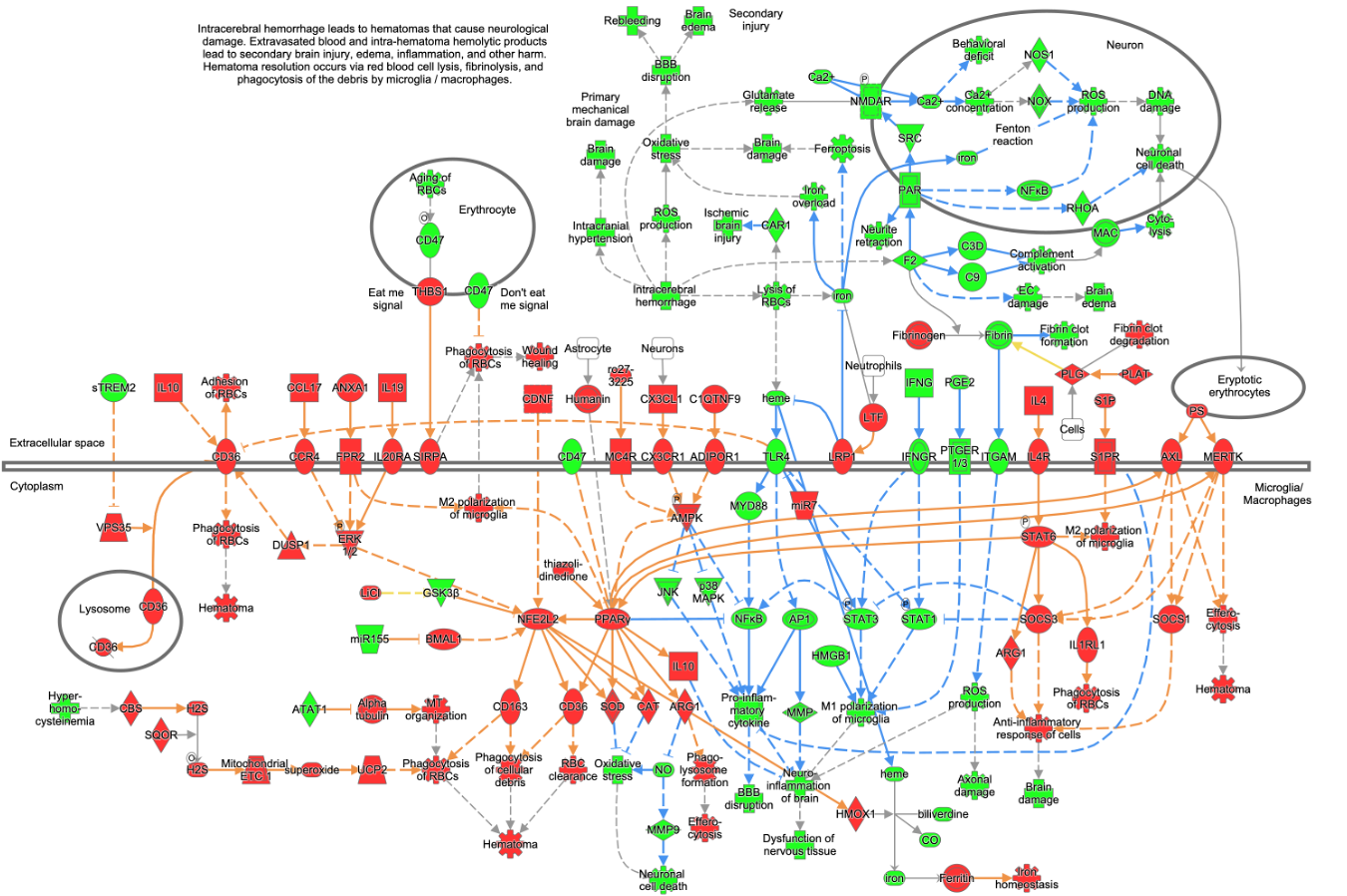
- Hematoma Resolution Signaling Pathway
- Histone Modification Signaling Pathway
- Nuclear Cytoskeleton Signaling Pathway
Signaling pathways with Activity Pattern added and content updated
- Cellular Effects of Sildenafil
- Ephrin A Signaling Pathway
- Hereditary Breast Cancer Signaling Pathway
- Parkinson’s Signaling Pathway
Figure 2. Example of a new Canonical Pathway in the release. This figure shows the Hematoma Resolution Signaling Pathway. The pathway nodes are overlaid with colors that indicate their expected activity if the pathway were activated, where red indicates activated and green indicates inhibited. For example, PPARγ is colored red, indicating that this protein would be expected to be activated in case of hematoma resolution (based on the underlying curated literature). In contrast, CD47 (colored green) is an inhibitor of the pathway and, therefore, should be inhibited if the pathway was activated.
>200,000 new findings for a total of >13.3 million
- >79,000 Expert findings (from literature curation)
- >20,900 Protein–protein interaction findings from BioGrid
- >81,000 Cancer mutation findings from ClinVar
- >15,300 Gene-to-disease findings from COSMIC
- >450 Protein–protein interaction findings from IntAct
- >1,700 Drug-to-disease findings from ClinicalTrials.gov
- >700 Target-to-disease findings from ClinicalTrials.gov
- >600 Gene-to-disease findings from the Online Inheritance in Man (OMIM)
- >230 Findings from Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen)
- >700 Gene Ontology findings
- 50 Newly mappable chemicals
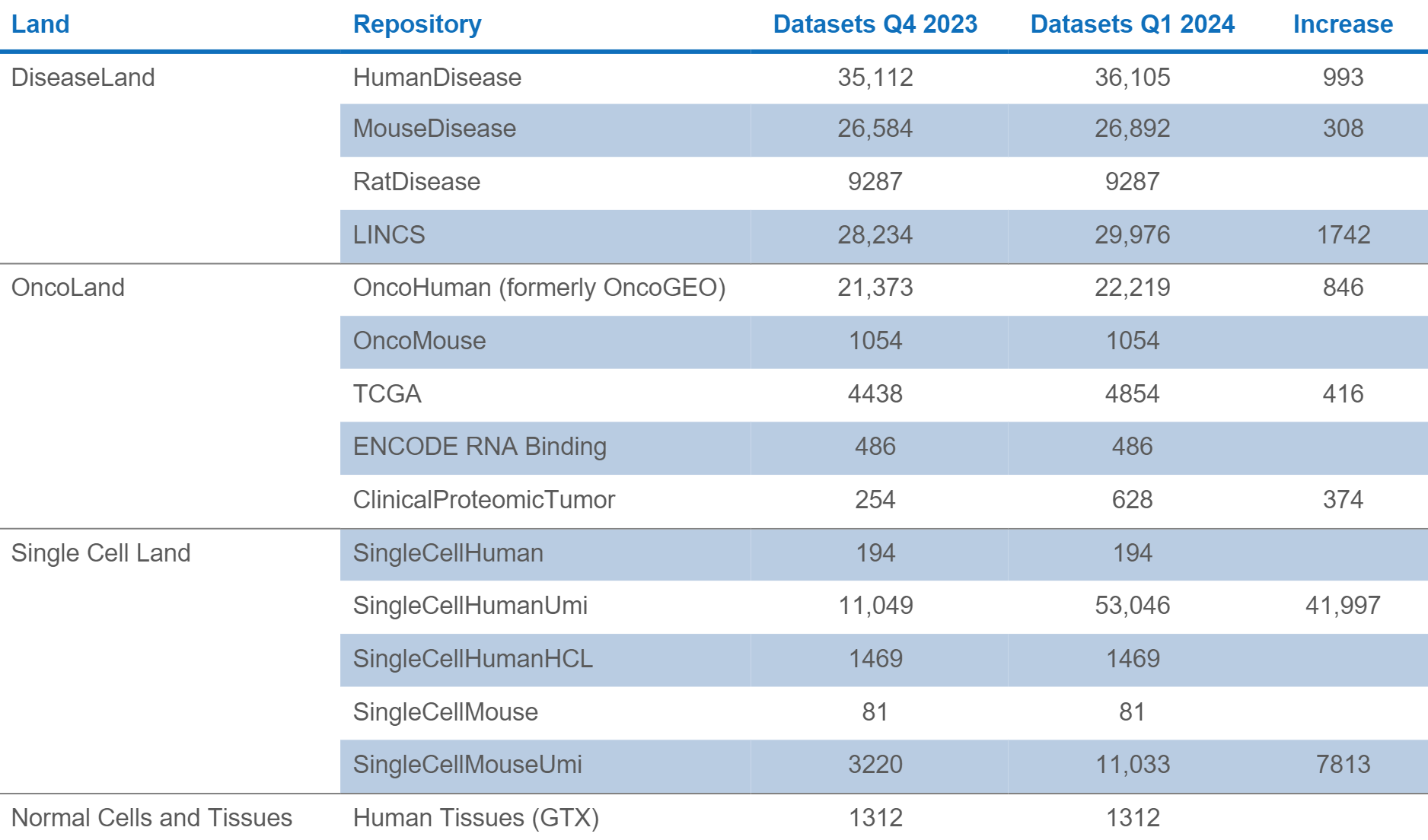
Analysis Match: 54,489 new datasets for a total of 198,636 datasets
Datasets and corresponding analyses will appear in IPA in late April 2024.
The LINCS (Library of Integrated Network-Based Cellular Signatures) datasets and analyses in this release replace the existing LINCS datasets and their analyses. LINCS represents a collection of transcriptional expression data of cells in response to perturbagens. The collection comprises cultured human cell lines treated with bioactive small molecules and genetic perturbation collected with the Broad Institute’s L1000 assay.
The original “fold change” LINCS data have been replaced in favor of replicate-collapsed Z-scores (level 5). The new datasets in IPA are a rationally chosen set of 29,976 comparisons from the total available in OmicSoft. The goal was to select a representative but low redundancy set from those with a relatively strong transcriptional response. The measure of transcriptional activity is represented as “TAS” or “transcriptional activity score”. Specifically, any perturbagen with at least one comparison with a max TAS greater than 0.2 is included. The comparison (dataset) with the greatest max TAS was selected. If there were comparisons with TAS > 0.33, each unique combination of drug x cell line x dose was included, up to a limit of 20 comparisons per perturbagen.
Update to Analysis Match datasets metadata
Users can quickly find which analyses from OmicSoft are new for a specific IPA release. A new metadata field called “OSLandedDate” (short for “OmicSoft Landed Date”) has been added to all OmicSoft datasets in IPA. The values in that field indicate when the datasets were curated and released by OmicSoft. For example, one of the most recent “landed dates” is referred to as 2023R4. As always, all OmicSoft analyses are re-run each quarter, so the date refers to roughly when they first appeared in IPA, not when they were last analyzed.
Removal of overly broad functions
Many broadly defined functions have always been excluded from being scored in a Core Analysis but still appeared in IPA in other contexts, such as when “growing” in networks. For example, IPA included a function called “Cell stage”, which is better described by more specific sub-functions such as “Mitosis”. Such functions were typically too broad to be useful (which is why they were excluded from analysis) and could lead to confusion when present in some areas of IPA but not in analyses. These overly broad functions have now been removed from grow and connect and other “graph” operations in IPA.

 Archive
Archive